Taxation of Natural Persons under the UAE’s Corporate Tax Law

In the dynamic landscape of taxation in the United Arab Emirates, a significant shift has occurred with the introduction of Federal Decree-Law No. 47 of 2022 on the Taxation of Corporations and Businesses (known as the ‘UAE CT Law’). While the UAE remains known for its absence of personal income tax, the new tax legislation marks a turning point by introducing corporate tax, which now extends to certain types of income earned by individuals, or ‘natural persons.’
This shift notably impacts natural persons engaged in various business activities, including freelancers, social media influencers, and self-employed professionals operating under specific licenses.
In this article, we will examine the ramifications of the UAE Corporate Tax for individuals. We’ll explain who comes under the purview of corporate taxation, which income streams are subject to taxation, and, perhaps most crucially, how individuals can effectively handle their corporate tax obligations in the UAE.
Defining ‘Natural Person’ in the Context of UAE Corporate Tax
Who is a Natural Person?
A ‘natural person’ refers to any living individual, regardless of age, whether residing in the UAE or elsewhere. In the context of the UAE’s Corporate Tax Law, certain individuals now find themselves subject to corporate tax regulations.
Examples of Taxable Natural Persons
- Freelancers: These are individuals offering services independently, without traditional employment ties.
- Self-Employed Professionals with Unlimited Liability Licenses: Professionals providing expert advice, operating under licenses that hold them fully liable for business debts and obligations.
- Business Owners with Unlimited Liability Licenses: Entrepreneurs who own and manage businesses under licenses that merge their personal and business liabilities.
- Social Media Influencers: These are individuals who leverage their online presence and influence as a business venture.
Natural persons come under corporate tax liability when they engage in a Business or Business Activity in the UAE, regardless of whether they operate with or without a license. Specifically, those operating under licenses of unlimited liability status are subject to corporate tax.
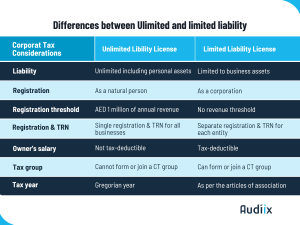
Understanding Unlimited Liability Licenses
Unlimited liability licenses merge the identity of the natural person and the business. In these scenarios, the individual’s direct control and full liability for the business’s debts make them the taxable entity, not the business itself.
Types of Unlimited Liability Licenses
- Sole Establishment
- Sole Proprietorship
- Freelance License or Permits.
- E-trader
Scope of Taxation for Natural Persons
The UAE’s Corporate Tax Law applies to natural persons involved in conducting a Business or Business Activity within the UAE, those with a Permanent Establishment in the UAE, or those deriving UAE Sourced Income.
A natural person is subject to Corporate Tax only when the total Turnover derived from all Business or Business Activities conducted in the UAE exceeds AED 1 million within a Gregorian calendar year.
Computation of Turnover Threshold
Turnover is calculated on a Gregorian calendar year basis, encompassing the gross income from all business activities. This includes income from sole proprietorships, freelancing, and the individual’s share from transparent Unincorporated Partnerships. The standard method for measuring turnover is the accrual basis of accounting, with exceptions for those using cash basis accounting.
Exclusions from Corporate Tax
Under the UAE Corporate Tax Law, specific categories of income are not classified as businesses or business activities. As a result, these income types are exempt from corporate taxation. These exemptions include:
- Wages: This includes all forms of employment compensation and benefits, such as director’s fees.
- Personal Investment Income: Income derived from investments made in a personal capacity, not requiring a business license or classified as a commercial business. Example: Earnings from investments in publicly traded securities.
- Real Estate Investment Income: Profits from selling, leasing, or renting real estate in the UAE, provided the activity doesn’t require a business license.
Corporate Tax Rates for Natural Persons
The corporate tax rate structure for natural persons is:
- 0% Tax Rate: Applied to the portion of taxable income that does not exceed AED 375,000.
- 9% Tax Rate: Imposed on the portion of taxable income exceeding AED 375,000.
Corporate Tax Return Filing for Natural Persons in UAE
Natural persons must submit their Corporate Tax Return to the Federal Tax Authority (FTA) within 9 months after the end of the relevant tax period. A single Tax Return should be filed for all natural person’s taxable businesses and business activities.
Essential Compliance Obligations for taxable Natural Persons
For natural persons whose business activities in the UAE generate more than AED 1 million, adherence to specific compliance requirements becomes essential. Understanding these obligations is crucial for ensuring conformity with the Corporate Tax framework. Here are the key responsibilities and processes that such individuals must follow to comply with corporate tax regulations:
- Tax Registration: Registration for Corporate Income Tax is mandatory when the taxable turnover surpasses AED 1 million within a Gregorian calendar year.
- Use of Tax Registration Number: A single Tax Registration Number is assigned upon registration, applicable to all existing and future business activities, negating the need for multiple registrations.
- Retaining Registration Status: Non-Deregistration for Lower Turnover: If the annual turnover dips below AED 1 million, deregistration is not an option unless all business activities are ceased.
- Annual Tax Filing and Payment: Filing Tax Returns: Tax returns must be filed annually within nine months following the end of the tax period.
- Applying for Reliefs: Electing for applicable reliefs, such as the Small Business Tax Relief for incomes not exceeding AED 3 million annually.
- Maintaining Accurate Records: Robust Accounting and Record keeping: Adequate record keeping is essential for aggregating all taxable income and capturing all tax-deductible expenses.

